Mainblades is a Dutch robotics software company focused on automated aircraft drone inspections. A technology that works inside and outside of aircraft maintenance hangars. This research focuses on deploying 5G technology to transform the conventional method of performing visual inspections, making it faster, more consistent and more accurate.
Duration
May – December 2023
Partners (TU Delft)
Do IoT Fieldlab, TU Delft
Partners (others)
Mainblades, TNO, MCS, SURF, Unmanned Valley, KLM
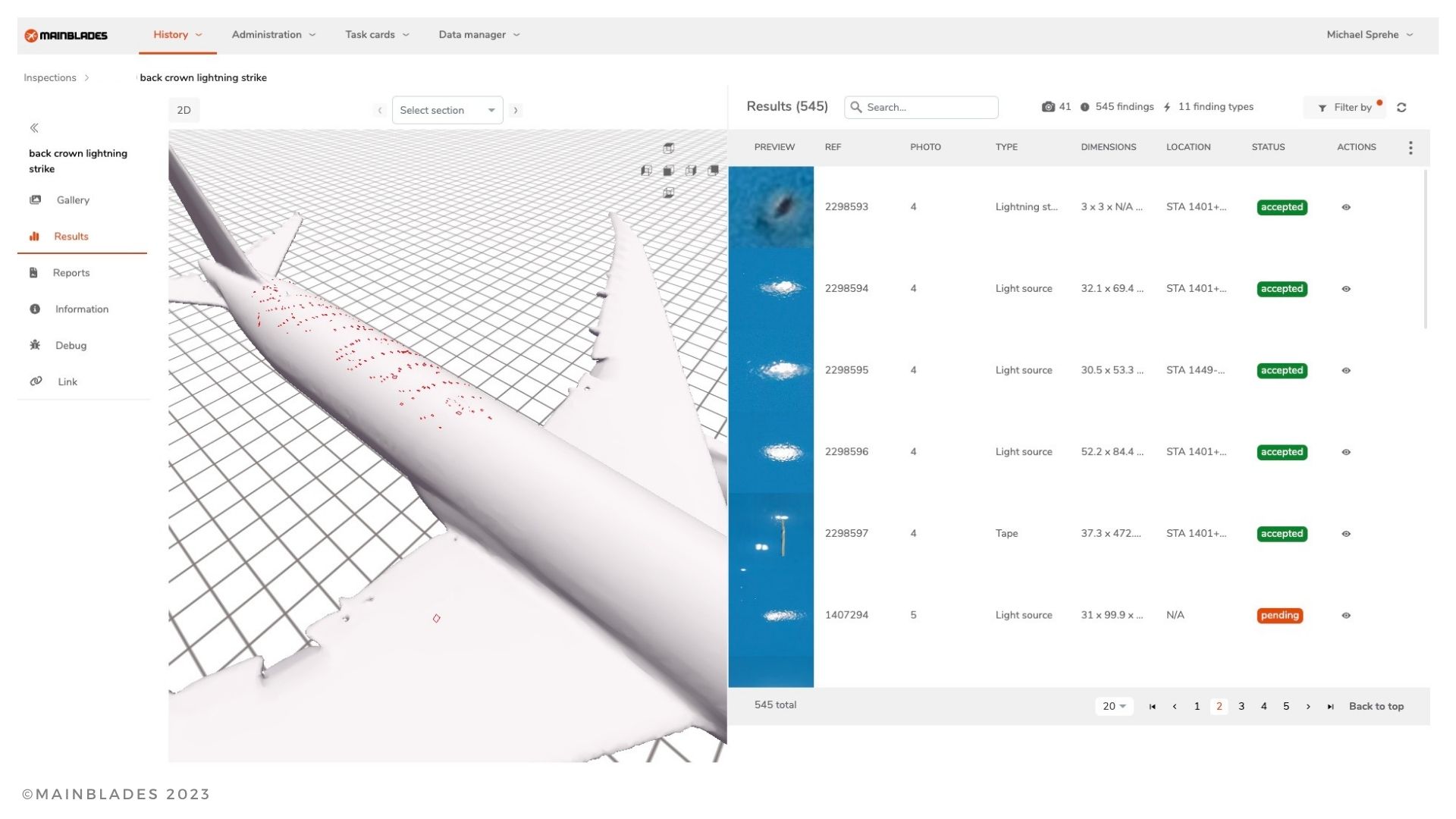
Every aircraft must be regularly inspected for anomalies. Mainblades combines visual drone inspections with artificial intelligence, to detect and identify small damages such as lightning strikes and paint peeling. Working with drones is faster than traditional inspections. By adding smart programming and AI to the process, the drones follow a fixed pattern for the inspections and can support with quick assessment of the images. For the aircraft MRO (maintenance, repair & overhaul) industry, a short and reliable maintenance process is key. Speeding up the process, without any concessions to accuracy is very valuable to get the aircraft faster ready for service. The technology also enables real-time data analysis, allowing maintenance teams to make more informed decisions about repairs and follow-up actions.
5G is crucial
The Mainblades product consists of hardware – a drone platform and control unit – and the software for processing and viewing the inspection data. The company explores the possibilities of a 5G network. The experiments consist of streaming sensor information from the camera and sensors directly to the cloud, instead of being transferred between the drone and the remote controller.
Using Do IoT field lab’s 5G facilities, Mainblades can safely perform tests with different types of modems and different network configurations. As safety regulations meet an extremely high standard on airports, an excellent connectivity and ultralow latency in data transfer are key. At the Unmanned Valley test site, Mainblades’ specialists can perform realistic tests and deploy improvements to further increase the speed of visual aircraft inspections. Furthermore, the coverage and reception of 5G on an airport and in hangars can be measured. The outcomes are relevant for maintenance in remote locations, where traditional connectivity options may not be available.
